- Name
- Doug Donovan
- dougdonovan@jhu.edu
- Office phone
- 443-997-9909
- Cell phone
- 443-462-2947
Who says you can't get hotter with age?
Researchers from Johns Hopkins University and other institutions have found that, on average, the temperature of galaxy clusters today is 4 million degrees Fahrenheit. That is 10 times hotter than 10 billion years ago, and four times hotter than the Sun's outermost atmosphere called the corona. The findings are published in the Astrophysical Journal.
"We have measured temperatures throughout the history of the universe," said Brice Ménard, a Johns Hopkins professor of physics and astronomy. "As time has gone on, all those clusters of galaxies are getting hotter and hotter because their gravity pulls more and more gas toward them."
Yi-Kuan Chiang, lead author of the study who was a Johns Hopkins post-doctoral researcher until moving to Ohio State University last year, added: "This drag is so violent that more and more gas is shocked and heated up."
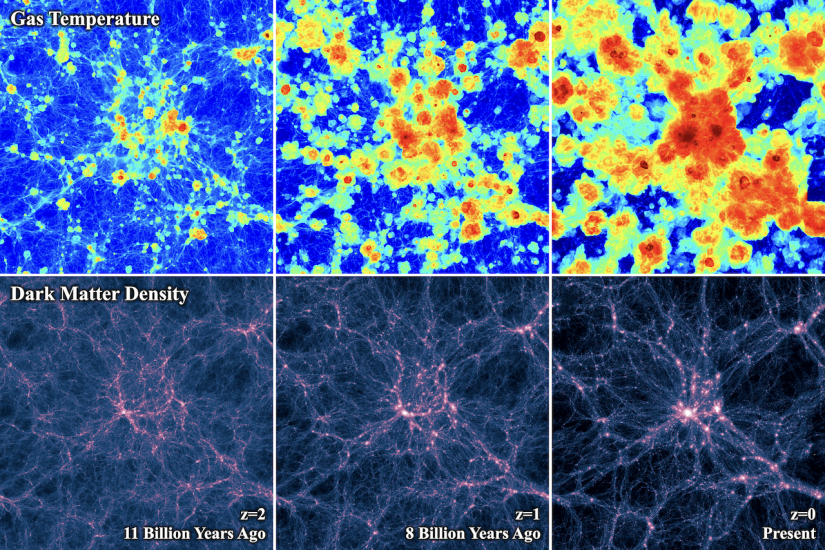
Image caption: As the universe evolves, matter concentrations are surrounded by gas halos getting hotter and bigger.
Image credit: D. Nelson / Illustris Collaboration
Imagine all those gas atoms being sucked towards galaxies like they were myriads of meteoroids piercing Earth's atmosphere, Ménard said. They accelerate as gravity pulls them toward the Earth's surface and heat up due to friction with the atmosphere before burning into what are seen as shooting stars, he added. This pattern of heating due to gravitational forces can be applied to entire galaxies, clusters of galaxies, and beyond into the "large scale structures" of the universe formed by gravity—a theory attributed to James Peebles, the 2019 Nobel laureate in physics.
"Our measurements are a great confirmation of that theory," Ménard said.
To perform this analysis, the team used data collected by the astronomical community over two decades, first from a telescope on the ground that conducted the Sloan Digital Sky Survey and then the Planck mission, a space telescope led by the European Space Agency.
The team used a technique that Ménard developed with Chiang. With it, they estimated the "redshift" of gas concentrations seen in images of microwave light going back in time all the way to 10 billion years ago. "Redshift" describes the way wavelengths of light lengthen due to the expansion of the universe. The farther away something is, the longer its wavelength—and the older its origin.
The method allowed them to measure the gradual increase in the gas temperature as a function of the age of the universe. This trend is also predicted by numerical simulations showing how dark matter and the atoms present in the gas evolve with time. As illustrated in the figure, these visualizations show gas temperatures changing from a cool blue canvas from 10 billion years ago into one speckled with hot red today.
The warming of the universe has nothing to do with climate warming on Earth, Ménard said. It is a consequence of gravitational attraction that had been predicted but which now can be precisely measured with these novel techniques.
Posted in Science+Technology
Tagged astronomy, astrophysics, physics and astronomy, outer space