Science+Technology
We all shimmy like these electric fish
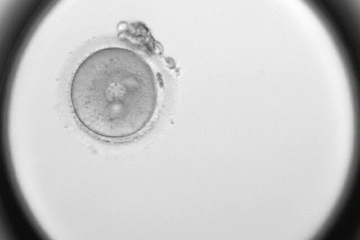
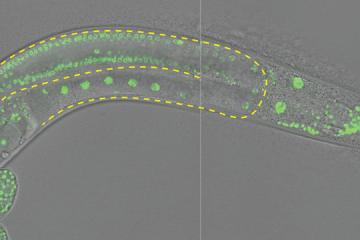
Published Oct 26, 2023Johns Hopkins scientists are the first to demonstrate that a wide range of organisms, even microbes, perform the same pattern of movements in order to sense their surroundings