Dorothy Ross, pioneering historian of the origins of modern social science and a professor emerita in the Johns Hopkins University Department of History, died last week. She was 87.
Ross's research focused on historical writing in the social sciences, revealing insights from the history of fields including psychology, economics, political science, and sociology that transformed scholars' understanding of the past. The depth of her dedication to graduate education was illustrated by her 2023 establishment of the New Directions Fund in the History Department to support graduate student research and conference travel.
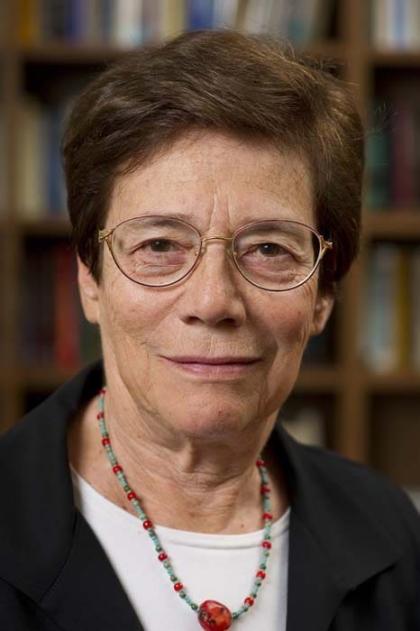

Image caption: Dorothy Ross
"Dorothy was an exemplary scholar, a generous mentor, and a kind colleague," said Tobie Meyer-Fong, professor and chair of the Department of History. "She was incredibly supportive of me when I first joined the department and continued to offer wise counsel as recently as this past semester. She was a role model both professionally and personally: She was an ambitious and brilliant historian, an outstanding teacher of graduate students, a loving wife, a devoted mother and grandmother, and a kind and caring friend. She made it seem possible and desirable to have both professional and family commitments."
In her 1991 book, The Origins of American Social Science, Ross examined how American social science modeled itself on natural science and liberal politics, arguing that the field was informed by the ideology of American exceptionalism, and tracing how each discipline responded to change in historical consciousness, political needs, professional structures, and available conceptions of science. As editor of Modernist Impulses in the Human Sciences, 1870-1930 (1994), she explored modernism in the human sciences, philosophy, and natural sciences in the context of the debate at that time—generated by the advent of postmodernism—about modernism in intellectual history and throughout the humanities.
"Dorothy's work was authoritative, wide-ranging, and scrupulously fair, even as she revealed all the problems that emerged as the social sciences became increasingly ahistorical and individualistic," said Angus Burgin, associate professor in the Department of History. "As a teacher and colleague she wore her extraordinary depth of learning lightly, approaching everyone she encountered with respect, honesty, and a seriousness of purpose. Spending time with her was always a reminder of why we chose to become historians." In his role at the SNF Agora's Center for Economy and Society, Burgin recently had the opportunity to name a foundation-funded endowed chair, which he named in Ross's honor.
"Her scholarship was formidable. The sheer erudition in her work is breathtaking," said François Furstenberg, A&S '03 (PhD), professor in the Department of History, who earned his doctorate under Ross's guidance. "Her scholarship was theoretically and indeed philosophically informed and empirically rich. I have read and re-read her work and now, nearly 30 years after first reading it, I still find more to learn and admire."
Deeply committed to outstanding graduate education, Ross was known for intensely engaging with her students' research and for the example of her powerful and questioning intellect. Her ferocious intellect and exacting questions were balanced by her intellectual and personal generosity and wry sense of humor.
"Dorothy was a smart, generous, and very patient person," said Motoe Sasaki, A&S '01 (MA), '09 (PhD), who is now associate professor on the Faculty of Intercultural Communication at Hosei University in Tokyo. "She was not the type of professor who just explained things to students. I recall many times she let students find their own way to make sense of specific academic issues or problems. When I was unsure of things, Dorothy would bombard me with questions from a number of perspectives so that I could realize the direction in which to proceed. This always brought me to a new place."
In 2002, Kenneth Moss met Ross when he presented a paper to the history department as a candidate for a faculty position, quickly learning the level of precise thinking she demanded. "She pointed to a single word in the paper and demanded (in a friendly tone but one that brooked no evasion) that I unpack exactly what I meant to say with it," he said. "The word was 'visceral.' This was in no way a picayune or trivial question, nor an unfair one; in fact, she had zeroed in on the pivotal moment in the paper's argument, and indeed a central moment in the argument of what became my first book."
Moss got the job, serving as a professor of modern Jewish history from 2003 to 2021 and becoming Ross's friend as well as colleague. He is now a professor of Jewish history in the Department of History at the University of Chicago.
"Dorothy had an unfailingly friendly and gracious manner with people," Moss said, "but I think that everyone who met her saw from the very first that she had a razor-sharp mind, demanded intellectual precision—and had a finely tuned bull**** detector. Her acuity, precision, and love of careful thinking will be missed."
Earlier this year, Louis Hyman was named the history department's inaugural Dorothy Ross Professor of Political Economy and Professor at the Agora Institute. In his remarks, he highlighted how Ross's research—especially in The Origins of American Social Science—showed that separating history from social science drastically inhibits what policy is able to accomplish.
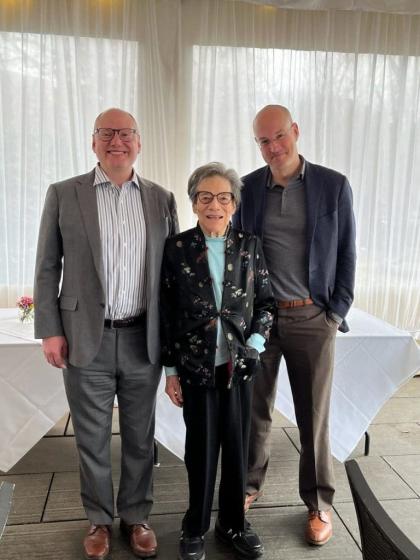

Image caption: From left, Louis Hyman, Dorothy Ross, and Angus Burgin on Feb. 22 at Hyman's installation as the inaugural Dorothy Ross Professor of Political Economy in History and Professor at the SNF Agora Institute
"Her work remains as a touchstone because it centered the texts (so many texts!) in her analysis. She didn't celebrate or denounce, for instance, the rise of marginalism in economic thought, but explained it in ways that restored happenstance and social structure to a narrative that had, to that point, just treated its rise as a scientific inevitability," Hyman said. "She historicized. In a time when it was easy to slip into fashionable theories, her combination of close and wide reading created in Origins an enduring classic of American intellectual history, that showed just how American our intellectual history was."
At the same time that she was knocking down barriers in social thinking and blazing historiographic trails, Ross was also doing those things within academia. Having joined the history department in 1990, she was the first woman, in 1993, to be named its chair, serving in that position until 1996. She and several other women hired as full professors at that time had a profound effect on the department, Meyer-Fong said.
A native of Milwaukee, Wisconsin, Ross earned a bachelor's degree at Smith College in 1958, and master's and doctoral degrees at Columbia University in 1959 and 1965, respectively. Before coming to Hopkins, she served as assistant professor of history at Princeton from 1972 to 1978, including a stint as Philip and Beulah Rollins Bicentennial Preceptor from 1973 to 1976; and as associate professor and then professor at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, from 1978 to 1990.
She previously served as a fellow in history and psychiatry at Cornell University Medical College-Payne Whitney Clinic from 1965 to 1967, and as special assistant to the Committee on Women Historians at the American Historical Association from 1971 to 1972.
Ross was a Fellow at the Center for Advanced Study in Behavioral Sciences, the Society of American Historians, and the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars; and a member of the American Studies Association, History of Science Society, American History Association, and Organization of American Historians, where she also served on the executive board. She edited the Johns Hopkins University Press series called New Studies in American Intellectual and Cultural History. She served on the editorial boards of the Journal of the History of Ideas, Rethinking History, Modern Intellectual History, and Cambridge University Press's Ideas in Context series. She was a delegate to the American Historical Association to the Consortium of Social Science Associations, and chaired the Organization of American Historians' Ellis Hawley Prize Committee.
Posted in Arts+Culture, Politics+Society
Tagged history, krieger school, obituary