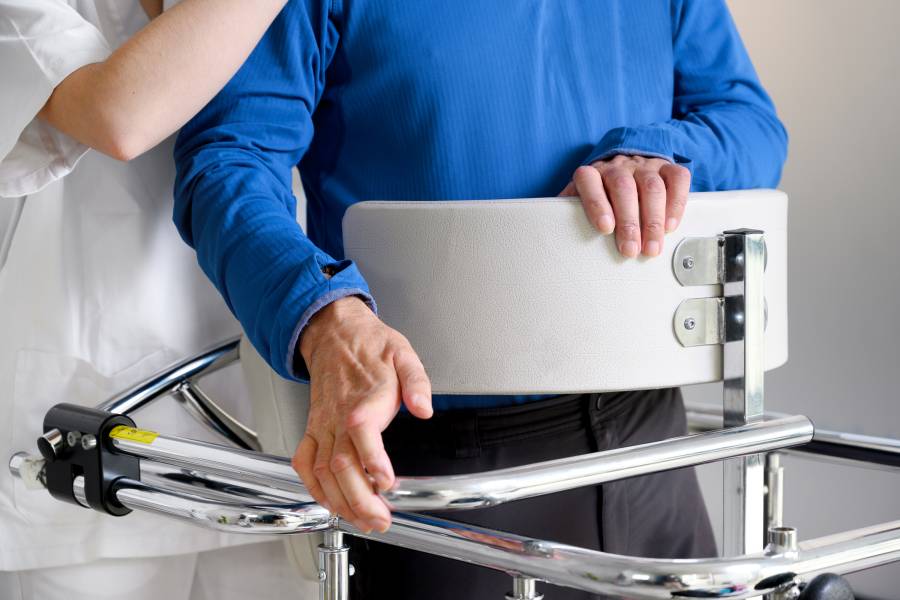
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or ALS, is a neurodegenerative disorder that weakens muscles over time, impacting physical function and ultimately leading to death. There is no single cause for the disease and no known cure. However, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers have found a possible window of opportunity during ALS treatment to target cells within the central nervous system that affect vital motor function.
The research team believes that a subtype of cells called astrocytes is actively involved in the death of motor neurons, which allow people to move, speak, swallow, and breathe by sending commands from the brain to the muscles that carry out these functions. Dysfunction within astrocytes could therefore be a viable target for ALS treatment.
"We think this is particularly important because the astrocyte dysfunction is active after symptom onset in patients with ALS," says Nicholas Maragakis, professor of neurology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and medical director of the Johns Hopkins ALS clinical trials unit. "This finding may enable us to target abnormalities in astrocytes for ALS treatment."
In their study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers analyzed brain and spinal cord tissues from patients with ALS and observed that a particular astrocyte protein, connexin 43, acts as an open pore that sends toxic factors to the motor neurons from the astrocytes. The pore was particularly active in patients with ALS who have a family history of the disease and those who contracted the disease in a sporadic fashion.
The research team was also able to develop stem cell lines from patients with ALS and develop them into astrocytes. They found that these astrocytes induced motor neuron death through hemichannels, proteins that provide pathways for the movement of molecules among cells.
"This is a new pathway that we have shown to be present in ALS tissues, animal models, and patient-derived stem cells," Maragakis says. "It's also exciting that this particular hemichannel protein seems to be elevated in spinal fluid from patients with ALS and could serve as an important biomarker. This is a true precision medicine approach toward the disease."
ALS affects as many as 30,000 people in the United States, with 5,000 new cases diagnosed each year. Pharmaceuticals are being developed that could block this hemichannel, Maragakis says, and during the study, his team showed that tonabersat, a drug originally developed to treat migraines and epilepsy, could block astrocyte-induced motor neuron death in human ALS stem cell lines and animal models.
The study offers increasing evidence that astrocytes play a role in the spread of ALS. Next, the team will try to establish why this hemichannel is so active in ALS astrocytes, giving them a better understanding of how the disease progresses. Maragakis says it's equally important because it furthers his team's work to identify new drugs that can block this particular hemichannel, serving as future therapeutics for ALS.