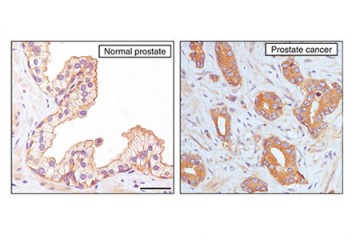
Brain science
Serotonin: The key to unlocking Alzheimer's?
Published Aug 18, 2017Brain scan study from School of Medicine adds to evidence that lower brain serotonin levels are linked to Alzheimer's and other forms of dementia
/ School of Medicine