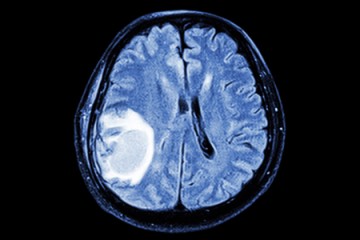
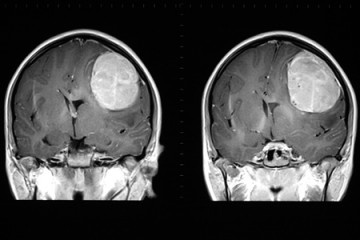
Brain cancer
This gel stops brain tumors in mice. Could it offer hope for humans?
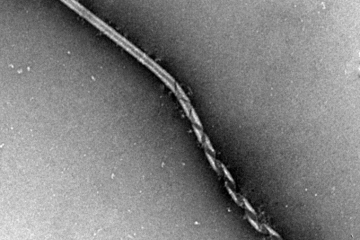
Published April 24, 2023The gel can reach areas that surgery might miss and current drugs struggle to reach to kill lingering cancer cells and suppress tumor growth